Token không đáng kể Bitcoin (NFT) đã thu hút sự chú ý của thế giới crypto nhanh chóng, mở ra những cơ hội mới cho những người đam mê nghệ thuật số và blockchain lâu đời nhất. Kể từ khi bùng nổ vào năm 2020, NFT thường được đúc và giao dịch trên các nền tảng dựa trên Ethereum, bên cạnh các blockchain khác, chẳng hạn như Cardano và Solana.
Tuy nhiên, một giao thức mới được gọi là Ordinals đã được đưa ra vào tháng 1 năm 2023 bởi cựu đóng góp Bitcoin Core Casey Rodarmor, người đã khai thác bản nâng cấp Bitcoin Taproot 2021 để mở rộng khả năng tiền điện tử và cho phép trên chuỗi Bitcoin-Native NFT.
Taproot cung cấp một cách để mở rộng khả năng khối của lớp cơ sở bằng cách ngưng tụ kích thước của các giao dịch đòi hỏi ít sử dụng dữ liệu hơn và khuyến khích việc sử dụng các hợp đồng thông minh trên Bitcoin. Việc nâng cấp làm tăng đáng kể các loại giao dịch có thể trên Bitcoin, bao gồm tài chính phi tập trung (DeFi) và các ứng dụng NFT.
Đến tháng 2 năm 2023, nhà phát hành NFT lớn nhất thế giới, Yuga Labs, đã công bố việc tạo ra TwelveFold, một bộ sưu tập NFT mới được phát hành trên Bitcoin, qua đó ủng hộ Bitcoin NFs và avouching thành công của họ.
Dưới đây là những gì bạn cần biết về Bitcoin NFT, cách chúng khác với phương pháp thay thế dựa trên Ethereum phổ biến nhất và cách tạo và bán chúng.
Phối lệnh là gì?
Các số thứ tự là số sê-ri được in dấu trong một satoshi (sat) duy nhất, đơn vị nhỏ nhất của Bitcoin (BTC), thông qua lý thuyết thứ tự gán chúng theo thứ tự mà chúng được khai thác. Satoshi đầu tiên trong khối thứ nhất có số thứ tự 0, thứ hai có số thứ tự 1, và satoshi cuối cùng của khối thứ nhất có số thứ tự 4,999,999,999.
Tiền xu màu là đại diện đầu tiên của một khái niệm như vậy trở lại vào năm 2012, là tài sản crypto được tái sử dụng để đại diện cho một cái gì đó có giá trị bằng cách thêm thông tin siêu dữ liệu. Counterparty là một nỗ lực khác để nhúng dữ liệu vào các giao dịch Bitcoin thông thường. Tuy nhiên, nó có mã thông báo XCP riêng, được yêu cầu cho một số chức năng, làm cho nó chính thức giống như một altcoin và không phải là một phần mở rộng hoặc lớp thứ hai cho Bitcoin.
Lý thuyết thứ tự thưởng cho satoshis với giá trị numismatic, cho phép chúng được thu thập và giao dịch như hiếm. Satoshis được cung cấp danh tính cá nhân để được theo dõi, chuyển giao và ăn sâu với dữ liệu tùy ý có ý nghĩa, chẳng hạn như hình ảnh, văn bản hoặc video, thông qua một giao dịch Bitcoin vẫn là một phần vĩnh viễn của blockchain. Dữ liệu như vậy có thể được xem trong ví tương thích với Ordinals, chẳng hạn như ví Sparrow, và các nhà thám hiểm trực tuyến.
Chữ khắc
Quá trình giao tài sản cho satoshis cá nhân được gọi là dòng chữ. Chữ khắc là những hiện vật kỹ thuật số có nguồn gốc từ blockchain Bitcoin, tương đương kỹ thuật số của các hiện vật vật lý.
Họ hoàn toàn trên chuỗi, không yêu cầu một sidechain hoặc một token riêng biệt, và sử dụng giao thức Ordinals để ghi sats với nội dung trên ord, một chỉ số, một nhà thám hiểm và một ví mà dựa vào Bitcoin Core để quản lý khóa riêng và ký giao dịch.
Ord cho phép theo dõi vị trí của satoshis cụ thể và số thứ tự của chúng và có thể được xem với thám hiểm Ordinals. Ngược lại với NFT truyền thống dựa vào nội dung off-chain được lưu trữ trên hệ thống tập tin liên hành tinh (IPFS), các chữ khắc có năng khiếu với tính bất biến và bảo mật của Bitcoin. Chúng là những hiện vật kỹ thuật số không cho phép và không kiểm duyệt vì chúng có thể được bán mà không có tiền bản quyền.
Làm thế nào để tạo Bitcoin NFT
Hệ sinh thái Ordinals đang được phát triển đầy đủ, nhưng khả năng tiếp cận của nó vẫn bị hạn chế ở hai cách chính để bạc hà một NFT thứ tự.
Phương pháp đầu tiên để khắc Bitcoin Ordinals đòi hỏi một số kỹ năng kỹ thuật, chạy một nút Bitcoin đầy đủ và sau đó cài đặt Ord trên nút này để ghi satoshis vào một ví Ordinals và làm cho Bitcoin Ordinals NFT. Hai loại ví Bitcoin có thể xử lý Ordinals; cả hai đều phải tương thích với Taproot và có khả năng “kiểm soát đồng xu” để tránh chi tiêu satoshis Ordinal như phí mạng hoặc gửi chúng vô tình trong một giao dịch khác.
- Ví Sparrow chỉ được khuyến khích để nhận Ordinals để tránh gửi Ordinals sats vô tình. Tuy nhiên, sử dụng nó không yêu cầu chạy một nút đầy đủ. Dưới đây là cách thiết lập một ví Sparrow.
- Một ví Ord yêu cầu chạy một nút đầy đủ trên dung lượng 500GB. Không giống như ví Sparrow, ví Ord cho phép bạn tạo chữ khắc và đóng băng các sats được ghi để tránh tình cờ chi tiêu. Dưới đây là cách thiết lập ví Ord.
Bất kể bạn đang sử dụng ví nào, hãy đảm bảo có một số Bitcoin sẵn có để thanh toán phí giao dịch.
Phương pháp thứ hai đơn giản hơn và liên quan đến việc sử dụng một công cụ không có mã, chẳng hạn như Gamma hoặc Ordinalsbot.com, để ghi NFT thứ tự của bạn. Dưới đây là cách bạc hà Ordinal của bạn trên Gamma:
- Chọn loại tập tin bạn muốn sử dụng để bạc hà Bitcoin NFT của bạn.
- Tải lên tệp cần thiết từ máy tính của bạn.
- Thiết lập phí giao dịch tùy thuộc vào thời gian bạn muốn chờ đợi cho Ordinal của bạn được đúc.
- Sao chép và dán địa chỉ Bitcoin nơi để gửi các hiện vật kỹ thuật số, mà cần phải là một địa chỉ tương thích thông thường hoặc một địa chỉ Taproot.
- Đợi cho NFT được đúc. Việc chờ đợi như vậy phụ thuộc vào lệ phí bạn đã trả cho quá trình được hoàn thành và có thể là hàng giờ hoặc thậm chí cả ngày. Bạn sẽ có thể theo dõi trạng thái đúc tiền thông qua một liên kết mà bạn sẽ nhận được qua email.
- Xem số thứ tự đúc của bạn trên OrdinalsViewer.
How to trade Ordinals
While proper infrastructure and marketplaces to trade Bitcoin Ordinals are being built, the digital artifacts are traded peer-to-peer over-the-counter (OTC) in dedicated Discord servers, with escrows as intermediaries and tracked on Google sheets.
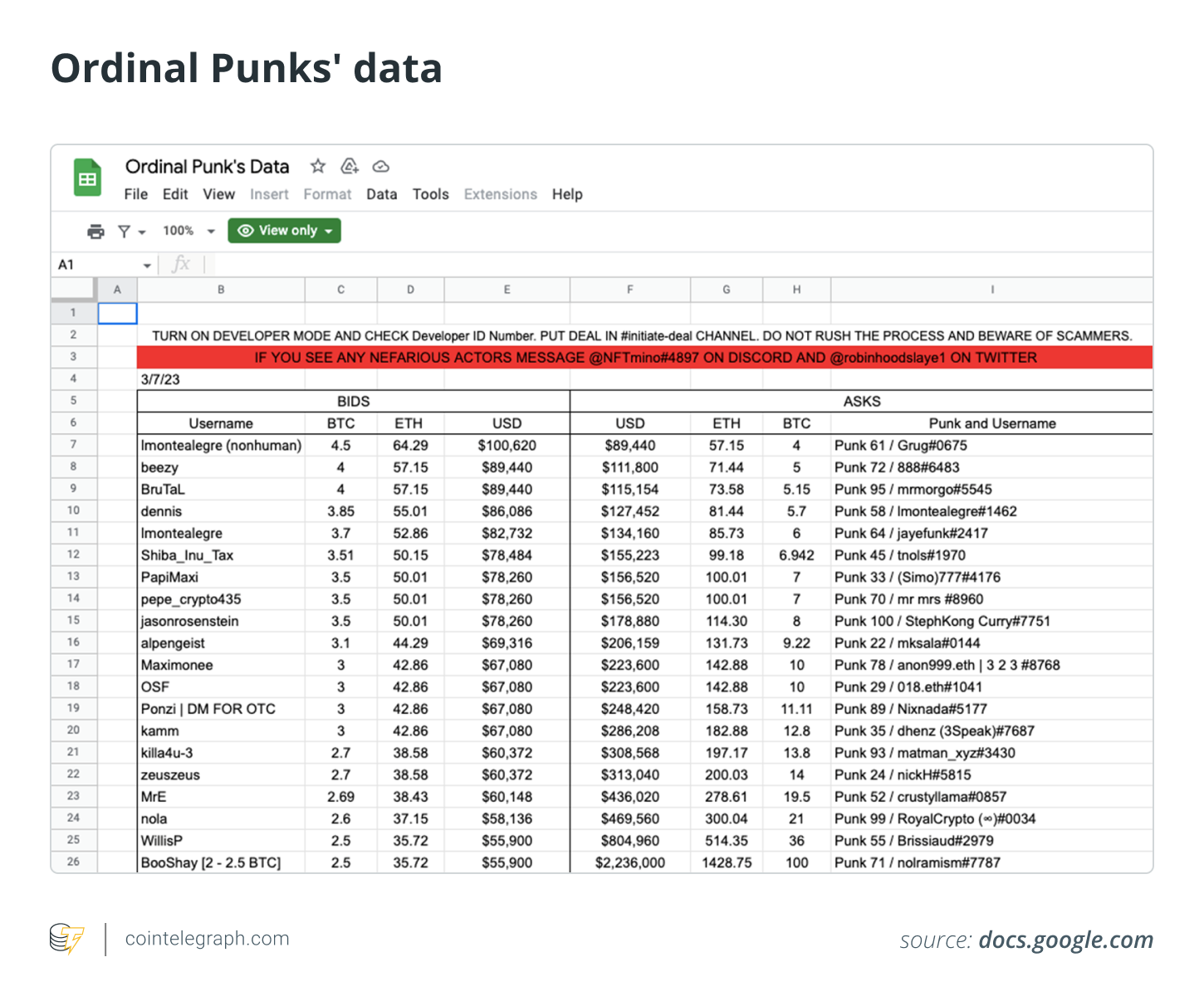
Compared to the more popular NFTs traded via Ethereum and other blockchains, Bitcoin Ordinals trading appears to be an obsolete method. Yet this hasn’t contained people’s interest in Bitcoin NFTs, with hundreds of thousands of newly minted digital artifacts emerging within only a few weeks from launch.
The Ordinals market is entirely trustless, using the secure, partially signed Bitcoin transactions (PSBT) technology, which allows users to easily sign transactions in cold storage, and atomic swaps with no intermediary and a market fee of 2.7%. A system to verify creators is being developed to include creator royalties of 4.2%.
How to buy Bitcoin NFTs
Taproot-compatible wallets must be used to buy Bitcoin Ordinals, such as the Ordinals wallet, the Xverse and Hiro wallets. The Ordinals wallet is very straightforward to use, and the others are also similar:
- Create an account, secure your seed phrase, and deposit funds into the wallet.
- Select the Ordinals you wish to purchase and click “Buy Now.”
- Once the transaction has been executed, the Ordinals will be added to your wallet.
How to sell Bitcoin NFTs
Similar to buying a Bitcoin NFT, you’ll need to pick a Bitcoin Taproot-compatible wallet and download it.
- Create an account, secure your seed phrase, and upload your inscription. The fee will depend on the file size and how fast you’d like the transaction completed.
- Once your file has been inscribed onto the blockchain, you can view it on the Ordinals.com inscriptions page.
- You can freeze the Ordinals to make sure you do not spend them.
- You’ll need to use a peer-to-peer OTC market, usually, the Bitcoin Ordinals Discord server, to sell your inscription.
It is recommended that particular attention is placed on these trades. Being in an unregulated peer-to-peer OTC market, platforms are full of scammers trying to catch the latest Bitcoin NFT craze.
Ordinals vs. traditional NFTs
A few differences distance Ethereum-based traditional NFTs from Bitcoin Ordinals, although they both tend to be grouped under the same umbrella of digital art. The creator of Bitcoin Ordinals, Casey Rodarmor, defines Bitcoin NFTs as authentic digital artifacts because they are on-chain and enjoy all of the good properties Bitcoin holds. Here are the main differences:
- Bitcoin inscriptions are always immutable, while Ethereum-based NFTs can technically be changed or deleted by the contract owner. Traditional NFTs must be audited to become immutable, which requires deep knowledge of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Solidity.
- Bitcoin inscriptions always have on-chain content, making it impossible to be lost. It is durable and scarcer because inscription creators must pay fees proportional to the size of the content. In contrast, Ethereum NFT content can be off-chain and stored on platforms such as IPFS and could be lost.
- Bitcoin inscriptions are more secure because the blockchain is the most secure. Inscriptions can be sold with PSBT without needing a third party, such as an exchange or marketplace, to transfer them on the user’s behalf. On the other hand, Ethereum NFTs tend to grant intermediary platforms unlimited permission over a user’s NFT, and the use of complex smart contracts may be challenging to interact with for the regular non-techie who wants to trade digital art.
Unlike NFTs, which are minted as completely new tokens, Ordinals have the raw file data inscribed directly onto the sats on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Bitcoin NFTs controversy
The new Ordinals protocol has raised an important question and sparked a heated debate among the NFT community. Should Bitcoin just be money, or should it expand its functionality to other use cases? Is the Ordinals protocol an attack on the Bitcoin network?
The Bitcoin blockchain has traditionally been used only for payment transactions due to its limited block size and network architecture. Such infrastructure favors solutions built on top of the blockchain as additional layers to increase the network’s programmability and scalability.
The latest Ordinals craze has raised many eyebrows among the BTC community. Some are concerned it could distract from Bitcoin’s primary use case as a medium of exchange and whether Ordinals make good use of block space. Ordinals can be images, audio clips or even games inevitably requiring space that is subtracted from the financial data, significantly slowing down on-chain confirmation times.
Bitcoin’s fungibility
Bitcoin’s fungibility — one of the main properties of money — is also challenged by Ordinals. This is because inscriptions are imprinted in one satoshi, making it a rare unit, just like numismatic coins are rare physical objects used for collections.
Ordinal satoshis become individual identities that can be tracked, transferred and imbued with meaningful information, such as text or an image, making the sat unique and turning it into a de facto NFT. On the other hand, the traditional stance views all satoshis as equal, or they begin to lose a significant trait of money.
Full node costs
A few weeks after the project was launched, a record-breaking-sized block of 4MB was created, raising concerns among the community about the future efficiency and costs of the blockchain and its full nodes. The average size of a Bitcoin block had never exceeded 1.5MB until the launch of Ordinal NFTs.
Inscription contrarians fear that increasing the Bitcoin blockchain size due to the big transactions and blocks would raise the requirements and costs for devices running a full node. The counterargument is that for the Bitcoin blockchain to be securer, its blocks must be full, which would justify users paying a higher fee.
The debate will unfold in the future as the Ordinals market takes a more robust shape and new opportunities arise. Ultimately, Bitcoin’s true spirit and value reside in its resilience to guide the market in the direction the people want.

























